Marginal cost
The increase or decrease in a firm's total cost of production as a result of changing production by one unit.
Copyright © 2012, Campbell R. Harvey. All Rights Reserved.
Marginal Cost
The total cost to a company to produce one more unit of a product. The marginal cost varies according to how many more or fewer units a company wishes to produce. Increasing production may increase or decrease the marginal cost, because the marginal cost includes all costs such as labor, materials, and the cost of infrastructure. For example, if a widget manufacturer increases the number of widgets it produces, it may need to buy more material, but the costs of labor and factory maintenance remain the same, and are spread out over a greater number of widgets. This may reduce the marginal cost. On the other hand, if the manufacturer hires more workers and builds another factory, it will likely increase the marginal cost. It is also known as the incremental cost.
Farlex Financial Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All Rights Reserved
marginal cost
The additional cost needed to produce or purchase one more unit of a good or service. For example, if a firm can produce 150 units of a product at a total cost of $5,000 and 151 units for $5,100, the marginal cost of the 151st unit is $100. Industries with sharply declining marginal costs tend to be made up of firms that engage in price wars to gain market share. For example, the airlines often discount fares to fill empty seats with customers from competing airlines. Also called incremental cost.
Wall Street Words: An A to Z Guide to Investment Terms for Today's Investor by David L. Scott. Copyright © 2003 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. All rights reserved.
marginal cost
the extra cost that is incurred by a firm in increasing OUTPUT by one unit. Given that FIXED COSTS do not vary with output, marginal costs are entirely marginal VARIABLE COSTS. Marginal cost generally includes the DIRECT MATERIALS and DIRECT LABOUR COST of a product along with VARIABLE OVERHEADS. See MARGINAL REVENUE.Collins Dictionary of Business, 3rd ed. © 2002, 2005 C Pass, B Lowes, A Pendleton, L Chadwick, D O’Reilly and M Afferson
marginal cost
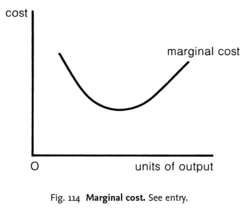
the extra cost (addition to TOTAL COST) that is incurred in the SHORT RUN in increasing OUTPUT by one unit. Given that FIXED COSTS do not vary with output, marginal costs (MC) are entirely marginal VARIABLE COSTS. MC falls at first, reflecting increasing RETURNS TO THE VARIABLE-FACTOR INPUT so that costs increase more slowly than output, as shown in Fig. 114. However, MC then rises as decreasing returns set in so that costs increase faster than output.MC together with MARGINAL REVENUE determine the level of output at which the firm attains PROFIT MAXIMIZATION.
Collins Dictionary of Economics, 4th ed. © C. Pass, B. Lowes, L. Davies 2005