income-elasticity of demand
see ELASTICITY OF DEMAND.Collins Dictionary of Business, 3rd ed. © 2002, 2005 C Pass, B Lowes, A Pendleton, L Chadwick, D O’Reilly and M Afferson
income-elasticity of demand
a measure of the degree of responsiveness of DEMAND to a given change in INCOME:
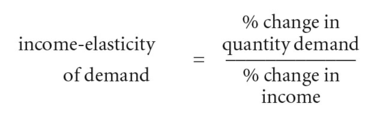
If a given change in income results in a more than proportional change in quantity demanded, then demand is said to be income-elastic, while if a given change in income results in a less than proportional change in quantity demanded, then demand is income-inelastic.
Income-elasticity is positive for a NORMAL PRODUCT and negative for an INFERIOR PRODUCT. STAPLE PRODUCTS tend to have an income-elasticity of demand of less than 1, whereas LUXURY PRODUCTS generally tend to have an income-elasticity of more than 1. See ENGEL'S LAW, INCOME EFFECT, INCOME-CONSUMPTION CURVE, DEMAND CURVE ( SHIFT IN).
Collins Dictionary of Economics, 4th ed. © C. Pass, B. Lowes, L. Davies 2005